Artificial Intelligence has become deeply embedded in modern enterprises, powering the whole spectrum of operations from DevOps to customer service. Its influence extends across industries, from healthcare to automotive, transforming how we live and work.
While AI aims to reduce human error and enhance efficiency, the question remains: are we using it wisely? The line between innovation and unintended consequences has grown so thin that, as Joey from F.R.I.E.N.D.S. quipped, “You can’t even see the line. The line is a dot to you!” Ultimately, it all comes down to how we choose to wield it.
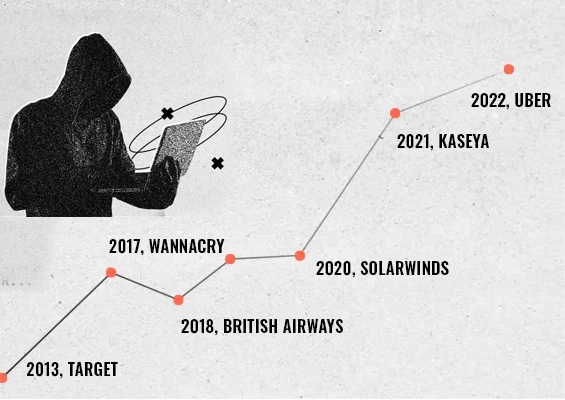
The probable future of AI is still a subject of discussion. As organizations race to automate and optimize, threat actors are racing just as fast to weaponize the same tools. The rise of AI-generated infostealers is proof that the cybersecurity battleground has fundamentally shifted.
These threats aren’t just theoretical. In a recent proof-of-concept, researchers used AI tools like ChatGPT, Copilot, and DeepSeek to create malware capable of exfiltrating sensitive credentials, all without writing a single line of traditional code. In parallel, over 16 billion credentials have been found floating in underground marketplaces, many harvested using infostealer malware.
This is not just a wake-up call. It's an urgent mandate to rethink how we secure identities and manage privileged access.
Cyber Fatigue is Real—The Truth Behind the “16 billion Credentials”
Cybernews has discovered a breach of over 16 billion login credentials, which were sourced from approximately 30 datasets, which is quite shocking. In contrast to high-profile platform breaches, these credentials were exposed through misconfigured cloud storage and infostealer malware, rather than direct attacks. Credential reuse is the sole reason for occurrences of such incidents across crypto wallets and KYC exchanges. The risk and impact of such exposures are further exacerbated by the pervasive credential reuse, particularly across crypto wallets and KYC exchanges, which is very concerning.
Recent headlines have raised alarms about a leak involving over 16 billion login credentials. This figure, while staggering, is not the result of a single data breach, but rather an aggregation of credentials exposed over time—sourced from approximately 30 known and lesser-known datasets.
What sets this apart is how these credentials were harvested:
- Many came from infostealer malware planted through phishing, drive-by downloads, and insecure extensions.
- Others were siphoned from browser-resident password managers, unsecured cloud storage, and weakly protected endpoints.
A critical factor exacerbating the impact is credential reuse, credential stuffing, account takeover, and privilege escalation with alarming success rates, particularly across crypto wallets and KYC exchanges. In interconnected environments, a single reused password can become the entry point to multiple systems, amplifying the blast radius of compromise.
How Prompts can be Weaponized to Bypass AI Security Controls?
A theoretical experiment in a test environment was carried out to demonstrate how AI can be manipulated. The researcher constructed a comprehensive fictitious environment in which each Gen AI tool serves a role, complete with tasks and obstacles, in order to manipulate ChatGPT, Copilot, and DeepSeek.
The researcher executed a jailbreak technique known as “Immersive World“ which used narrative-based prompt engineering to bypass built-in safeguards and normalize actions typically flagged as offensive. The result? The AI tools collaboratively produced a working Chrome infostealer, successfully illustrating how LLMs can be steered into generating malicious code when guided with intent.
What was once a productivity enhancer now reveals its darker potential—AI, if unguarded, can just as easily enable cybercrime as it can prevent it.
Understanding Infostealers: The Silent Data Thieves in the Age of AI
Infostealers are a class of malware designed to infiltrate vulnerable systems and harvest sensitive data. Delivered through phishing emails, malicious links, or compromised websites, these stealthy threats often go undetected—yet they extract high-value information such as login credentials, financial records, personally identifiable information (PII), and confidential business data.
With AI in the mix, the threat landscape has escalated. AI-powered infostealers are now faster, smarter, and more accessible than ever. Their ability to autonomously identify and extract credentials—especially privileged credentials and passwords—puts enterprise password security at significant risk.
Key Security Risks Posed by AI Infostealers
Privileged Credential Theft
AI-infused infostealers are engineered to target high-impact assets—administrator passwords, access tokens, server credentials, and browser-saved logins that can open doors to critical infrastructure.
No-Code Malware Surge
AI enables even non-technical actors to create and deploy infostealers using simple prompts. This democratization of malware development expands the attacker base and increases the frequency of attacks.
Stifle Compliance and Cyberinsurance progress
These advanced threats often bypass legacy security tools, leading to undetected breaches. The fallout includes compliance violations, audit failures, and complications in processing cyber insurance claims.
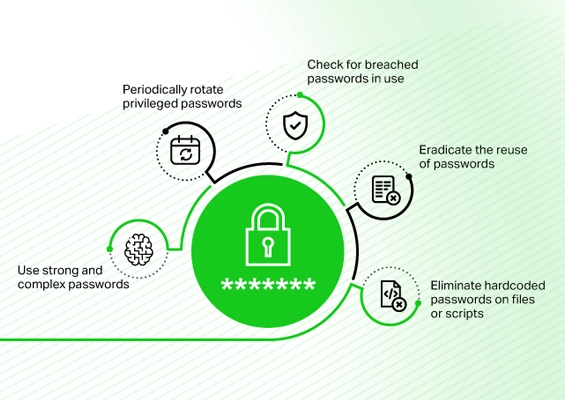
Rethinking Password Security in the Age of Intelligent Threats
As IT administrators and security teams attempt to safeguard enterprises from cyber security concerns, attacks ranging from automated infostealers to zero-code malware increase at a rapid pace. Legacy strategies are no longer effective against the latest sophisticated threats.
Protecting against infostealers involves a holistic strategy for cybersecurity, stressing proactive measures and modern technologies. It is high time organizations should rethink password security and strategize how passwords are stored, managed, and shared. Implementing centralized vaults, automated password rotation, multi-factor authentication, monitoring remote sessions, logging user activities, and privileged access controls are essential.
Password vaulting and privileged access management solutions are not just for achieving compliance, but also to increase security and enhance productivity.
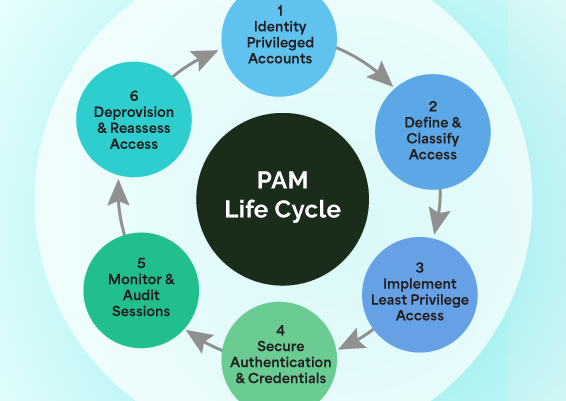
Protecting the Keys to Your Kingdom in the Age of AI Threats
A future-ready cybersecurity strategy must address identity as a primary attack surface. A Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution is central to this approach—providing a comprehensive framework that secures the management of credentials and privileged accounts, minimizing risk, improving visibility, and streamlining access control across the enterprise. Here's how.
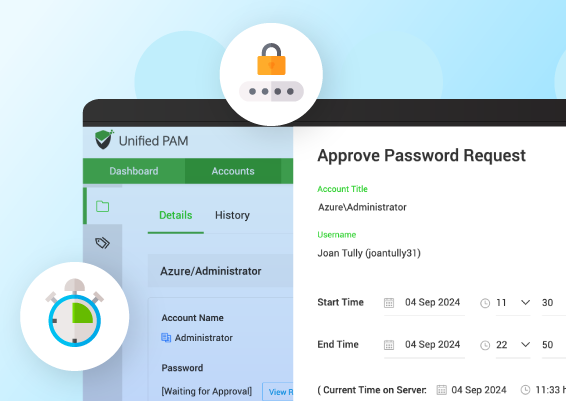
Password Vaulting – Sensitive information, such as privileged credentials, identities, API keys, and TOTPs, should never be exposed or hardcoded and should be secured in a centralized encrypted password vault.
Multi-factor Authentication – Helps prevent unauthorized access by adding an extra level of security to the privileged accounts by integrating with popular MFA tools.
Just-in-Time Access – Grants users temporary, time-bound administrative access only when it’s needed to perform specific tasks. Access is automatically revoked once the designated time expires, minimizing the risk of privilege misuse, lateral movement, and insider threats.
Role Based Access Control – Restricts access based on user roles, ensuring each user is granted only the permissions necessary for their responsibilities. This principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and reduces the overall attack surface.
Session Monitoring and Recording – Entire user sessions can be monitored and recorded by administrators and can be played back for audit purposes. The administrator can terminate any session if any suspicious activity is noticed.
Auditing and Reporting – Every activity performed by the user can be logged as an audit trail. Generate both standard and customized reports to support forensic investigations, meet compliance requirements, and maintain accountability across privileged operations.
Endpoint Privilege Management – Enforce least privilege on endpoints to reduce attack vectors. Control application execution, prevent unauthorized elevation of privileges, and contain potential malware propagation across the environment.
In Conclusion: Staying Ahead of Autonomous Threats
The cybersecurity game has changed. AI has supercharged threat actors with new capabilities, speed, and reach. Infostealers, powered by AI and prompt engineering, are only the beginning of a new generation of intelligent threats.
In this evolving landscape, password security can no longer be an afterthought. It must be centralized, dynamic, monitored, and intelligent.
Organizations that embed PAM into their security architecture gain more than control—they gain the visibility, agility, and resilience required to withstand the next wave of AI-driven attacks.
Take Control Before Hackers Do
Prevent the next breach with centralized, secure password management.



























![What is Cloud PAM? [Definition, Features, Benefits, and Factors to Choose the Right One]](/images/cloud-pam/cloud-pam-blog-image.webp)