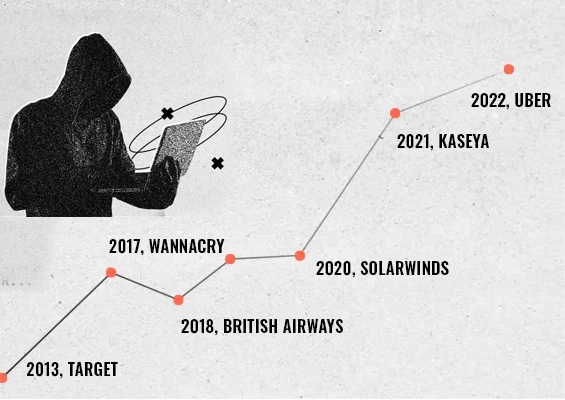
Passwords are omnipresent in our personal and business environments. An average person has around 100 passwords to remember for various accounts, and it is practically impossible to memorize unique, complex passwords for each of them. This leads to employees coming up with easy-to-remember passwords and reusing them for multiple accounts. Stolen, weak, or reused passwords are the top reasons for data breaches worldwide. It is up to the system administrators to ensure employees use strong and unique passwords for all their accounts.
Regulatory bodies and industry researchers publish information security guidelines to help organizations protect their passwords from cyberattacks. Some guidelines are industry-specific, and some others are industry-agnostic. But the objective of all the guidelines is to prevent cyberattacks and security breaches. Password security-related aspects find a place in almost all the guidelines. It makes sense to refer to these guidelines and adopt the best elements into your password policy, even if the guideline is not intended for your industry.
What is a password policy?
Password policy refers to the entire lifecycle of passwords - the way they are created, the complexity requirements, secure storage, safe transmission, periodic randomization, prompt deprovisioning, continuous monitoring, and more.
Password policies can define password complexity rules, such as length, character requirements, and expiration periods. Modern password managers allow the association of different password policies with various account types, enabling tailored security measures across the organization.
In this blog, we try to introduce you to some of the most popular information security guidelines published and share the top 10 policy recommendations that we think every system administrator should implement in their organization.
Why do you need a password policy?
A password policy is an important part of an organization’s security infrastructure. It is crucial for each and every employee to follow password guidelines to avoid the usage of weak, stolen, and repetitive passwords. Such passwords pave the way for unauthorized access to privileged accounts and many password-based attacks. A clear password policy safeguards sensitive accounts, encourages uniformity among teams, and facilitates adherence to industry standards. In the end, it lowers the possibility of security breaches by promoting better password usage throughout the organization.
What are the consequences of having poor password management?
A poor password can have a negative impact on the entire organization. Threat actors can easily invade the system and cause password-related attacks. Some of the are listed below:
- Credential stuffing: It is a type of cyberattack where threat actors gather a huge amount of credentials and inject them into website login forms.
- Password spraying: Password spraying is nothing but trying out the same password into many accounts before going to the next password.
- Brute-force attack: This is a trial-and-error method where attackers systematically try different combinations of characters, numbers, and symbols until the right password is found.
Password Security Standards and Guidelines
1. NIST SP800-63B
National Institute of Standards and Technology is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. It develops technology, standards, and best practices to ensure information security. NIST published its digital identity guidelines (NIST Special Publication 800-63B) in October 2017 and updated some of its sections in 2020. Section 5.1.1 (Memorized Secrets) of the document talks about passwords and how they should be managed and stored. Although it is meant for federal agencies to meet regulatory compliance requirements, every organization can benefit from implementing these guidelines.
Key NIST password guidelines
- Minimum length of 8 characters and maximum length of at least 64 characters if chosen by the user.
- Allow usage of ASCII characters (including space) and Unicode characters.
- Check prospective passwords against a list that contains values known to be commonly used, expected, or compromised. This includes passwords obtained from previous breach corpuses, dictionary Words, repetitive or sequential characters (‘aaaaaa’, ‘1234abcd’, etc.) and context-specific words, such as the name of the service, the username, and derivatives thereof.
- Limit consecutive failed authentication attempts on a single account to no more than 100.
- Allow "paste" functionality while entering a password.
- Provide a password strength meter.
- No complexity requirements or password expiration period.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Store passwords in a form resistant to offline attacks.
- Passwords shall be salted and hashed.
2. PCI DSS
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS Version 3.2.1) is a set of requirements to ensure sensitive data is protected, privacy is maintained, and networking systems are robust enough to withstand cyber-attacks. These guidelines are published by PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC). It is a global forum that brings together payments industry stakeholders to develop and drive the adoption of data security standards and resources for safe payments worldwide. PCI standards aren't specific to any one country or organization but rather function as a global set of standards that everyone can adhere to. Requirement 2 and 8 in the document talks about password requirements for logging into cardholder data environments.
Key PCI-DSS password guidelines
- Always change vendor-supplied defaults (passwords and settings) and remove or disable unnecessary default accounts before installing a system on the network (see 2.1).
- Remove/disable inactive user accounts within 90 days (see 8.1.4).
- Limit repeated access attempts by locking out the user ID after not more than six attempts (see 8.1.6).
- Set the lockout duration to a minimum of 30 minutes or until an administrator enables the user ID (see 8.1.7).
- If a session has been idle for more than 15 minutes, require the user to re-authenticate to re-activate the terminal or session (see 8.1.8).
- Passwords/passphrases must have a minimum length of 12 characters and must contain both numeric and alphabetic characters. (See 8.3.6)
- Passwords should have a minimum length of at least seven characters and contain both numeric and alphabetic characters (see 8.2.3).
- Change user passwords at least once every 90 days (see 8.2.4).
- Do not allow an individual to submit a new password that is the same as any of the last four passwords/passphrases they have used (see 8.2.5).
- Set passwords for first-time use and upon reset to a unique value for each user, and change immediately after the first use (see 8.2.6).
- Authenticate user access to assets with at least one of the following methods: password or a passphrase, any biometric method, Smart Card, or an authentication token. These authentication mechanisms must be encrypted during transmission and storage. (see 8.3.1.)
- Invalid authentication attempts are limited by: Locking out the user ID after not more than 10 attempts. Setting the lockout duration to a minimum of 30 minutes or until the user’s identity is confirmed. (See 8.3.4)
- Individuals are not allowed to submit a new password/passphrase that is the same as any of the last four passwords/passphrases used. (See 8.3.7)
- Change passwords/passphrases if there is any suspicion or knowledge that the password/passphrases have been compromised. (See 8.3.8)
- Implement and enforce MFA across all access into the CDE and for all remote access and document all MFA access (8.4.1 to 8.5.1)
- Passwords must not be hardcoded on scripts and must be periodically changed (8.6.2,8.6.3)
3. ISO/IEC 27002
ISO/IEC 27002:2013 is an information security standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is designed to be used as a reference for selecting security controls within the process of implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS). Control 5.17 within ISO 27002, enables organizations to properly allocate and manage authentication information, eliminate risks of failure in the authentication process and prevent security risks that may arise due to compromise of authentication information. Sections 9.2, 9.3, and 9.4 of the document talk about password guidelines to prevent unauthorized access to systems and applications.
Key ISO/IEC 27002 password guidelines
- Change default vendor secret authentication information after the installation of systems or software (see 9.2.4.g).
- Avoid keeping a record (e.g. on paper, software file or hand-held device) of secret authentication information unless this can be stored securely and the method of storing has been approved (e.g. password vault ) (see 9.3.1.b).
- When passwords are used as secret authentication information, select quality passwords with sufficient minimum length which are:
- easy to remember;
- not based on anything somebody else could easily guess or obtain using person related information, e.g. names, telephone numbers and dates of birth etc.;
- not vulnerable to dictionary attacks (i.e. do not consist of words included in dictionaries);
- free of consecutive identical, all-numeric or all-alphabetic characters; and
- if temporary, changed at the first log-on (see 9.3.1.d).
- Do not use the same secret authentication information for business and non-business purposes (see 9.3.1.g).
- Ensure proper protection of passwords when passwords are used as secret authentication information in automated log-on procedures and are stored (see 9.3.1.f).
- Password management systems should be interactive and should ensure quality passwords (see 9.4.3).
- Sensitive data such as passwords must be masked and prevented from leakage.
- Password management system implemented should:
- enforce the use of individual user IDs and passwords to maintain accountability;
- allow users to select and change their passwords and include a confirmation procedure to allow for input errors;
- enforce a choice of quality passwords;
- force users to change their passwords when they log-on for the first time;
- enforce regular password changes and as needed;
- maintain a record of previous user passwords and prevent reuse;
- do not display passwords on the screen when being entered;
- store password files separately from application system data; and
- store and transmit passwords in protected (encrypted or hashed) form (see 9.4.3).
4. CIS Password Policy Guide
CIS Password Policy Guide's objective is to be a single comprehensive password policy that can serve as a standard wherever a password policy is needed. It was published by the Center for Internet Security (CIS), a non-profit entity whose mission is to 'identify, develop, validate, promote, and sustain best practice solutions for cyber defense. They are responsible for the CIS Controls® and CIS Benchmarks™, globally recognized best practices for securing IT systems and data. It was last updated in December 2021, and has the following guidelines:
Key CIS Password guidelines
- Use MFA wherever possible (see 2.1).
- Require a minimum length of 14 characters for password-only accounts and 8 characters for MFA-enabled accounts (see 5.1.1).
- Maximum password length should be as long as possible based on system constraints (see 5.1.1).
- Do not limit the maximum length of passwords (see 5.1.1).
- Allow all character types in a password and require at least one non-alphabetic character for password-only accounts (see 5.1.2).
- Change the password immediately in the event of a breach, with an annual expiration as a backstop (see 5.1.3).
- Check on new password creation against an internal deny list of known bad, weak (Of at least 20 common passwords), or previous 5 passwords (see 5.1.4).
- Enforce a password change delay of at least one day (see 5.1.4).
- Lock current session after 15 minutes (or less) of inactivity (see 5.1.5).
- Temporary account lockout (15 minutes or more) after five consecutive failed attempts (see 5.1.6).
- Time doubling throttling (in minutes) between each retry (0, 1, 2, 4, 8, etc.) with a permanent account lockout (IT reset required) after 12 retries (see 5.1.6).
- Monitor and alert key personnel when the above bad login attempts reach the login limit (see 5.1.7).
- Automatically suspend the account after 45 days without a valid login (see 5.1.8).
- Do not allow user-defined password "hints" at login (see 5.1.9).
Optional Recommendations:
- Provide some form of password strength indication on creation (see 5.2.1).
- Allow display of entire password while creation and temporary display of each character while entering (see 5.2.2).
- Encourage the use of a password manager (see 5.2.3).
- Allow Paste in password fields when using a password manager (see 5.2.4).
5. NERC CIP
NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection (NERC-CIP) is a set of standards that specifies the minimum security requirements for bulk power systems. It was published by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), a non-profit international regulatory authority whose responsibility is to safeguard the reliability of the North American bulk power systems. Table R5 in the CIP-007-6 - Systems Security Management document talks in detail about the password policy requirements for power system operators.
Key NERC CIP Password guidelines
- Change known default passwords, per Cyber Asset capability (see 5.4).
- Password length that is, at least, the lesser of eight characters or the maximum length supported by the Cyber Asset (see 5.5.1).
- Minimum password complexity that is the lesser of three or more different types of characters (e.g., uppercase alphabetic, lowercase alphabetic, numeric, non-alphanumeric) or the maximum complexity supported by the Cyber Asset (see 5.5.2).
- Enforce password changes or an obligation to change the password at least once every 15 calendar months (see 5.6).
- Wherever possible, either limit the number of unsuccessful authentication attempts or generate alerts after a threshold of unsuccessful authentication attempts (see 5.7).
6. HIPAA Security Rule
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) is a federal law that required the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. HIPAA Security Rule describes how organizations must protect electronically protected health information (ePHI). HIPAA password requirements come under the Administrative Safeguards of the HIPAA Security Rule.
HIPAA Security Rule requires that organizations must implement procedures for creating, changing, and safeguarding passwords. It also recommends training the workforce on ways to safeguard password information and establish guidelines to create and change passwords in a periodic cycle.
HIPAA is intentionally does not offer specific password complexity guidelines. HIPAA doesn’t offer any specific password complexity guidelines, however, Security Standard §164.312(d) enforces organizations to implement procedures to verify the entity seeking access to electronically protected health information. To comply with HIPAA, organizations can opt to follow NIST password guidelines.
What are corporate password policies or business password policies?
Corporate password policies or business password policies are set of guidelines that help users ultimately create strong passwords that are hard to hack.
Corporate password policy examples
Some corporate password policy examples include setting password expiration dates and mentioning password complexity, penalties for violating set standards, how to store passwords, and lockout thresholds.
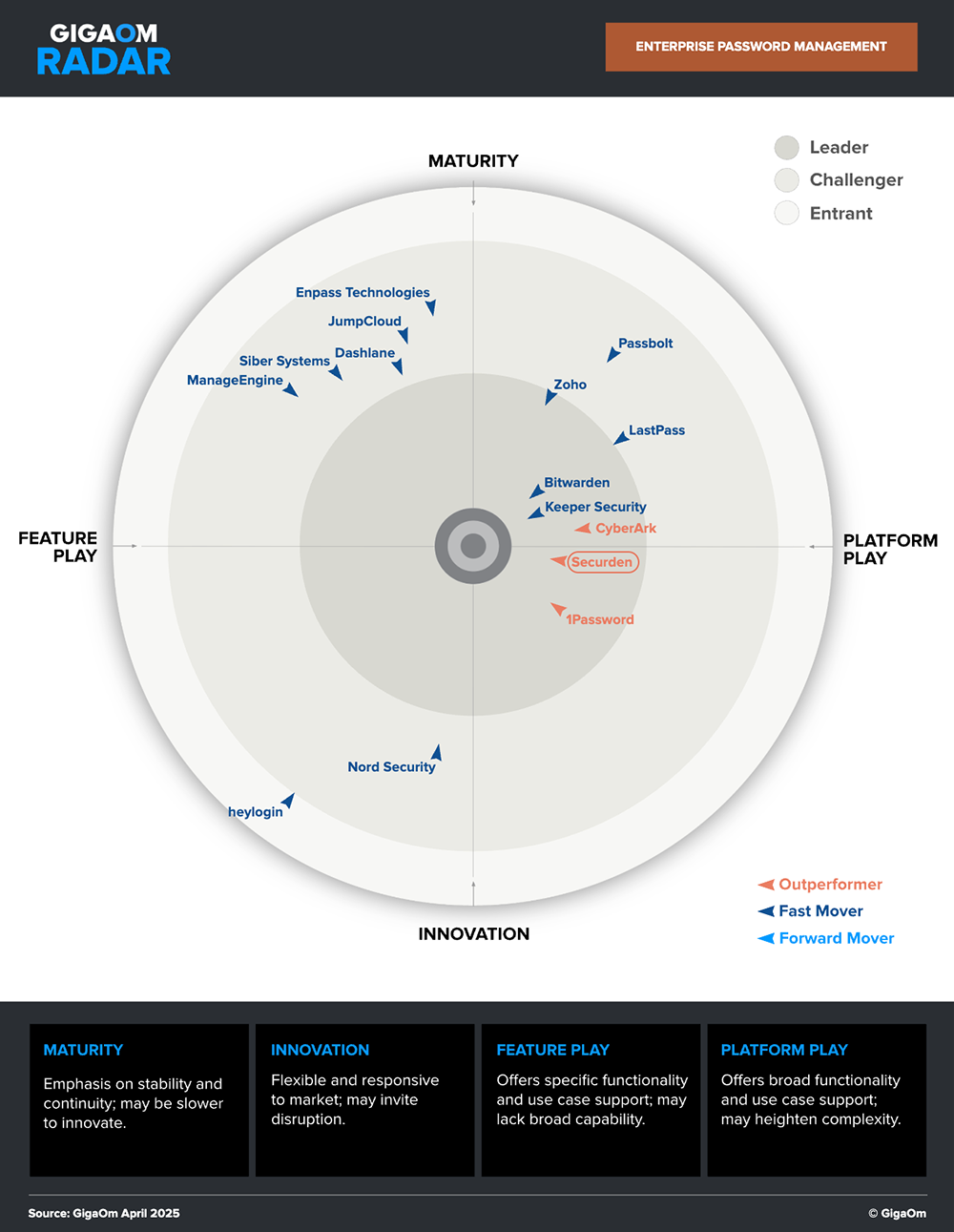
Securden is a market leader and an outperformer in the GigaOm Radar.
Corporate Password Policy Recommendations
Based on these password guidelines, here is a compilation of the top 10 password policy recommendations:
1. Use longer passwords
Hackers use methods like brute force attacks to gain access to your accounts. In a brute force attack, hackers run a program and check all possible combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols until the correct one is found. Every additional character increases the time it takes to crack a password exponentially. Adding numbers, symbols, upper and lowercase letters to the password makes it very difficult to brute force. Thus having a long, complex password is more secure.
Minimum password length in 2025
The best practice for password length is at least 12 characters, and it's better if it's more than 14 characters, comprising a mix of numbers, symbols, and mixed-case letters.

This chart, created by Hive Systems with data sourced from HowSecureIsMyPassword.net, shows how long it would take a hacker to "brute force" their way into your account, depending on the length of your password and the type characters included.
2. Do not reuse passwords
When large-scale data breaches occur, email addresses and passwords are often leaked online. If you reuse credentials across multiple accounts and one of them gets compromised, hackers can easily access your other accounts as well. When you pick a unique password for each account, even if hackers have credentials for one of your accounts, the rest of your accounts will remain secure. Also, avoid modifying and reusing the same passwords with a prefix or suffix (e.g., password1, password2).
3. Do not use personal information
Many people use names, birthdays, phone numbers, and other personal details in their passwords. While these are easy to remember, such data are readily available online and accessible to hackers. Use random combinations of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to increase your passwords' complexity and reduce the risk of a potential breach.
4. Change passwords in the event of a compromise
These days, we witness massive credential spills on a day-to-day basis. Whenever such an incident is reported, if you have ever dealt with the victim organization, immediately change the password used.
Passwords exposed in various data breaches worldwide are publicly available as a data dump. Many times, users are not aware when their passwords are exposed in credential spilling attacks. If a breached password is being used, it may lead to a spate of cyberattacks. You can use products like Securden Password Vault for Enterprises that proactively periodically scan the dump and check if any of the passwords stored in the product matches with the passwords that have been exposed in known data breaches.
According to the NIST compliance, the best practice for password change frequency is 365 days. It recommends longer password life as opposed to frequent 30–90-day password resets. Users when prompted to change passwords very soon intend to resort to old passwords with some appended strings. This in turn increases the vulnerability or chances of attack.
5. Check passwords against a list of commonly used, expected, or compromised passwords
One of the key recommendations in NIST SP800-63B password guidelines is to compare the prospective passwords against a list containing values known to be commonly used, expected, or compromised while changing a password. As mentioned above, products like Securden Password Vault for Enterprises can help you do this with ease.
6. Never text or email your passwords
When you share a username and password with someone over email or text, even if that person may not share it with anyone else, your credentials can get exposed if their email account or device gets compromised. Use secure methods like password managers to share passwords.
7. Avoid password recycling
Organizations should ensure that end-users do not recycle old passwords. The policy should enforce a minimum password age. Otherwise, end-users could change their password multiple times within a few minutes and reuse their previous password.
8. Establish password audits
You need to keep track of your team's compliance with the password security policy. Periodic audits help you to ensure password policy compliance and also to identify and change weak passwords.
9. Implement MFA
Multi-factor authentication provides you with an extra layer of security. It requires at least two authentication factors to access an account – something you know (a password), something you have (a one-time authentication code generated), and something you are (fingerprint). Always use multi-factor authentication when available. https://twofactorauth.org is a good reference point.
10. Start using a password manager
Maintaining an excel sheet or writing it down on a sheet of paper are dangerous ways to store your passwords. The most effective solution to maintaining overall password hygiene is to use a password manager. A password manager helps you create strong passwords based on the best practices for password policy mentioned above and securely store them.
Though implementing these recommendations won’t make you comply with the regulations mentioned above, these will serve as a good starting point in ensuring information security.
Best practices for team password management policy
When it comes to employee password management policies, following the password policy best practices are worth understanding. They include-
- Not saving passwords in plain text
- Not storing passwords in browsers
- Incorporating MFA and SSO integrations
- Setting maximum account login attempts
- Changing passwords to shared accounts when an employee departs
- Curtailing employees from accessing company servers using public machines
How does Securden, a password policy enforcement software help you apply a strong password policy?
While creating a strong password policy is important, you also need the right tools to implement the policy without any gaps across your organization. Securden Password Vault for Enterprises is a modern password policy enforcement software that helps you define a policy specifying the password strength and complexity requirements, periodicity for password resets, and other conditions. Once you define the policy, Securden helps in enforcing the policy in a fully automated fashion.
You can create any number of custom policies or use the predefined policies and assign them for different account types at a granular level. For example, you can enforce one policy for Windows servers, another policy for databases, and a different one for web accounts.
After defining policies, you can track the compliance status at the organization level. Securden offers actionable reports that show violations and the remedial measures that need to be taken.
Securden also helps you periodically check if any of the passwords stored matches the passwords uncovered in known data breaches. Whenever an unsafe password is detected, administrators, auditors, respective account owners, and other specific users can be alerted through email notifications.
Explore Securden’s Enterprise Password Vault
You can try Securden's Enterprise Password Vault for 30 days. Sign up for the cloud version or download the on-premise trial.
FAQs About Top 10 Password Policies
1. Should passwords be changed regularly?
Yes. According to traditional guidelines, passwords should be changed regularly on a periodic basis (30 – 90 days) to avoid the use of weak or stolen credentials. However, the new guidelines suggest passwords should be changed only if it is suspected to be breached.
2. Should users be allowed to paste passwords into login fields?
Yes. Users should allow login fields to paste passwords. This allows password managers to work efficiently without the need to view the passwords. To promote usability and password manager compatibility, NIST recommends allowing copy-paste.
3. How do password policies balance security and user convenience?
Password policies can balance security and user convenience by maintaining smooth password protection and reducing friction among the users. This balance between security and user convenience is important because strict password policies may cause discomfort and lead to the usage of weak and easy passwords.



























![What is Cloud PAM? [Definition, Features, Benefits, and Factors to Choose the Right One]](/images/cloud-pam/cloud-pam-blog-image.webp)