Mother of all breaches – Reinforces the need for enhanced password security
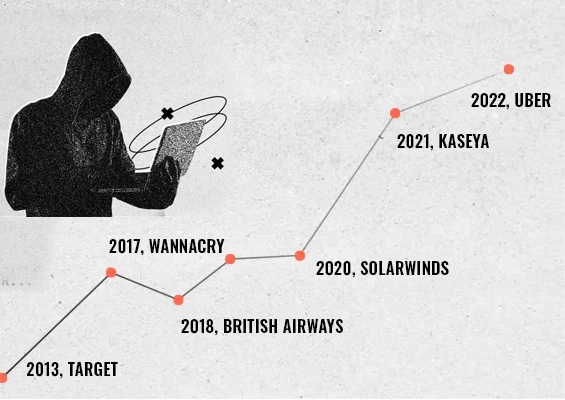
26 billion records have been leaked online. Yes, you read it right. Researchers from Security Discovery and CyberNews have stumbled upon this massive breach dubbed as the mother of all breaches (MOAB), running up to 12 terabytes in size and touted as the biggest data leaks found to date.
What’s all the data?
The supermassive MOAB does not contain newly stolen data but is mainly the largest compilation of multiple breaches (COMB) from the past. A previous COMB reported by CyberNews in 2021 contained 3.2 billion records, a mere 12% of the latest discovery.
The data contains records from Chinese messaging giants Tencent and Weibo and from Twitter, Dropbox, LinkedIn, Adobe, Canva, and Telegram. Researchers also claim that the leak includes records of government organizations in the US, Brazil, Germany, Philippines, Turkey, and other countries.
Possible threats from the super leak
The dataset is extremely dangerous; with all the leaked sensitive data freely available on the web, threat actors could use this opportunity to orchestrate a wide range of attacks like credential stuffing, identity theft, phishing attacks, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access to personal and sensitive accounts to name a few.
Compromised passwords often lead to data breaches
The volume of information made public may include passwords that have been hacked, which could result in data breaches by giving unauthorized users or threat actors access to privileged accounts, systems, and information in an organization.
These breaches often create a cyber-attack chain affecting organizations at every step:
Perimeter exploitation – Early attempts to gain unauthorized access using social engineering, credential stuffing, brute force password attacks, and stolen passwords to obtain login credentials.
Hijacking and escalation - Once within the organization's systems, the attacker will use various techniques, such as credential exploitation, to escalate privileges or control more systems or accounts.
Lateral movement – This is a stage where the attackers switch across systems laterally in an attempt to obtain sensitive information, privileged accounts, or vital resources.
How can organizations protect their passwords?
Deploying the most sophisticated security solution to thwart attacks is required but not enough. If basic access security best practices are ignored, the solution can always be compromised.
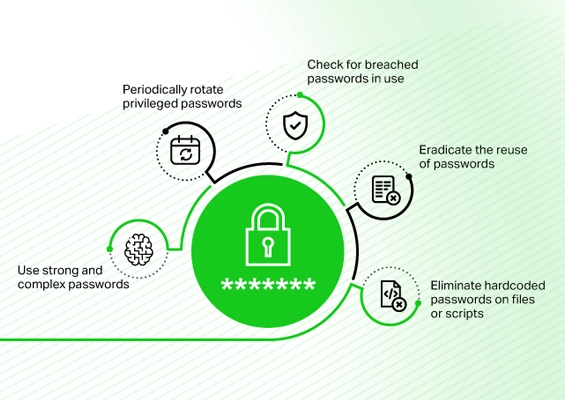
Password management best practices include: Maintaining password hygiene, eliminating hard-coded credentials, enforcing password complexity rules, and a robust password policy to prevent attackers from accessing critical systems.
Here are a few access security best practices on repeat mode that organizations should adhere to, even if they seem obvious.
- Monitor the dark web for breached passwords and eliminate their usage in the organization.
- Avoid reusing passwords and change them regularly.
- Establish and implement effective password policies within the organization.
- Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to access all sensitive assets. MFA acts as an additional layer of security and prevents identity compromises.
- Masking passwords while giving users access and utilizing APIs to fetch credentials.
- Monitor and record all user activity and send password activity logs to an SIEM solution to obtain actionable insights.
- Using an enterprise password management solution to secure all employee passwords.
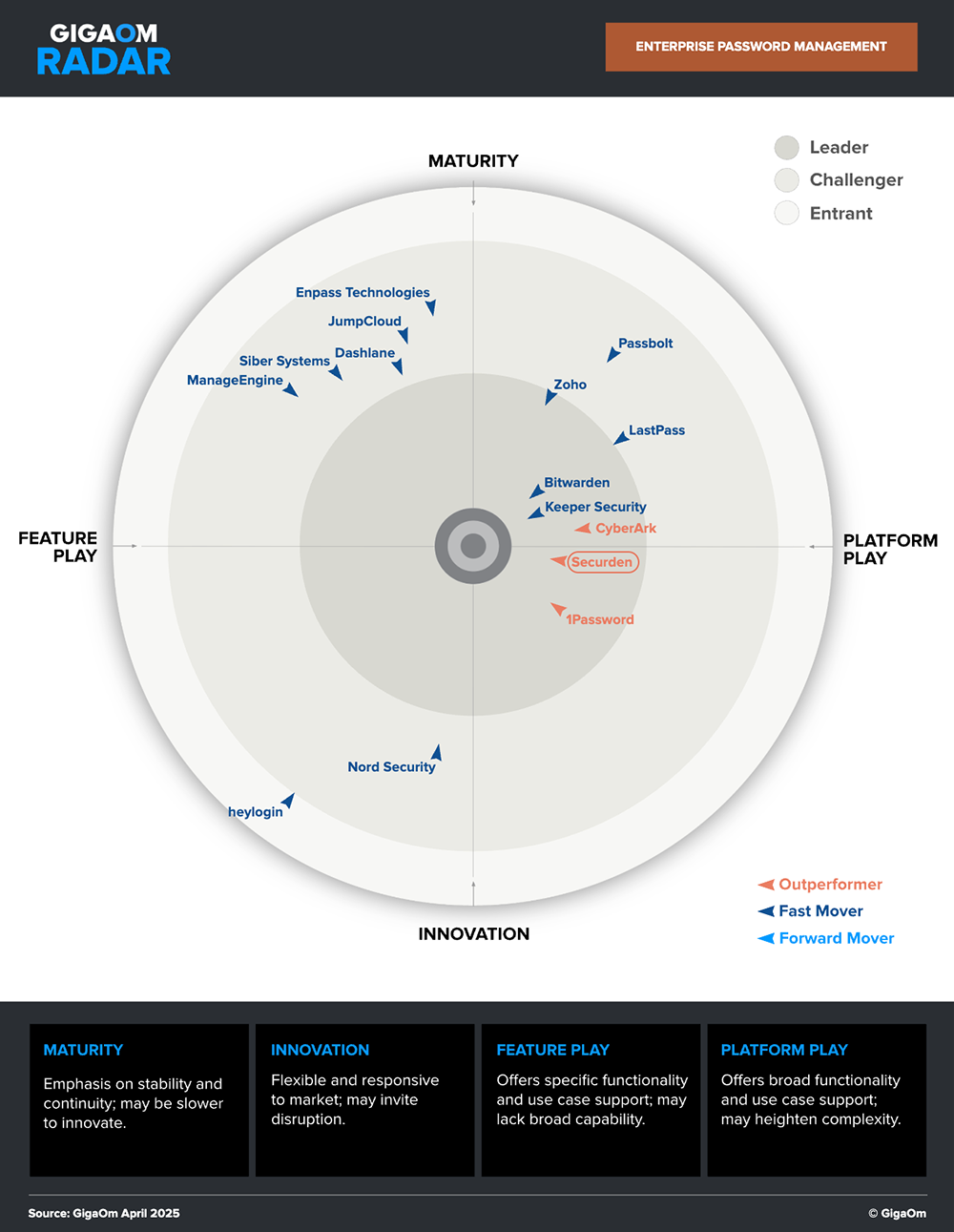
Securden is a market leader and an outperformer in the GigaOm Radar.
Defend against password-based attacks using Securden
The most sensitive information within an organization is its privileged credentials, which grant privileged access to critical accounts. Securden Enterprise Password Manager is a secured password vault that protects privileged passwords, SSH keys, DevOps secrets, workforce passwords, and more.
- Discover privileged accounts – Identify privileged accounts in computers, databases, and devices and assign strong and unique passwords.
- Secure storage - Lock all sensitive data in a digital vault fully encrypted.
- Centralized control - Defining who gets access to what.
- Multi-Factor Authentication - Add an extra layer of security in the authentication process.
- Just-in-Time access - Force users to raise a request every time they need access to an IT asset or an application
- Automated password rotation - Automate the entire process of randomizing passwords periodically. Securden will randomly generate a strong and unique password for every account.
- Audit trails – Gain visibility into the trail of activities like password access and changes across the organization
- All-round protection - Facilitates the prevention and defence against lateral movement, privilege escalation attacks, exposed hardcoded passwords, credential reusing attacks, account hijacking, and more.
Fixing the leaks
Even while modern technologies and a range of cybersecurity solutions are undoubtedly necessary for organizations, breaches usually result from neglecting security fundamentals.
Password security is the foundation of information security.
Organizations should enforce and automate these best practices to effectively reduce password attacks. These best practices can be automated using Password Management and Privileged Access Management solutions like Securden which offers an all-in-one platform for next-gen privileged access governance.
Prevent identity thefts, malware propagation, cyber-attacks, and insider exploitation. Try Securden today or request for a personalized demo.
Explore Securden’s Enterprise Password Vault
You can try Securden's Enterprise Password Vault for 30 days. Sign up for the cloud version or download the on-premise trial.



























![What is Cloud PAM? [Definition, Features, Benefits, and Factors to Choose the Right One]](/images/cloud-pam/cloud-pam-blog-image.webp)