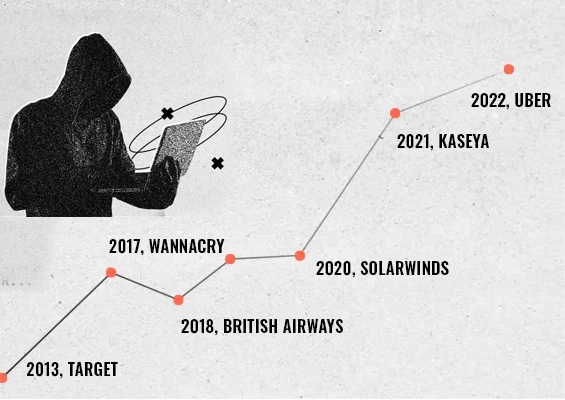
Passwords leaked from data breaches in the past continue to cause ripples in 2023, even amidst organizations with modern security standards. Poor password hygiene stands out as the culprit.
- Massive breach suffered by DraftKings, an American sports betting company.
- The accounts of 60,000 DraftKings users were hijacked by making use of stolen passwords from past breaches.
- Hackers walked away with around $600,000 from 1600 victim accounts.
The right keys unlock a multitude of doors
An 18-year-old hacker, Joseph Harrison, is alleged to have launched a credential-stuffing attack in November 2022 with a helping hand from a few others.
Joseph used a computer program to stuff credentials that were stolen from data breaches in the past. This involves repeatedly entering username-password combinations into websites until they crack into the login account. He is said to have had “69 wordlists which contained at least 38,484,088 individual username and password combinations”.
Once Joseph managed to crack into DraftKing user accounts, he marketed them and sold access to them on the internet. He even added instructions on bypassing two-factor authentication and draining funds from the compromised accounts.
A large number of such credential combinations are easily available on the dark web for anyone with the right tools to exploit. With the enormous amount of login data readily available on the internet, there is a good chance that simple passwords created by users are already present in the dark web database.
So often, weak, reused passwords are abused by cyber crooks and are used as a key for unlocking access to multiple websites, applications, and the sensitive data they hold.
Advancements in modern technology have complicated digital security. New studies reveal that AI can be used to crack passwords with relative ease. Novice hackers leverage powerful AI technology such as ChatGPT to learn step-by-step instructions on carrying out a cyberattack. Precautionary measures against new-age threats are essential to keep enterprises protected.
Gambling with password security is a bad bet
It is estimated that organizations will face around 33 billion account breaches in 2023. Leaning back and not giving importance to password security directly leads to organizations falling victim to massive breaches. IT teams and security engineers are too focused on implementing advanced security systems while they fail time and again to reinforce the building block of organizational safety – password security.
Neglected password hygiene spells disaster for enterprises
The world is overrun with novice hackers like 18-year-old Joseph, who believes that ‘Fraud is fun.’ Leveraging breached information from the internet, the teenager managed to loot thousands of dollars from users on DraftKings - simply because he was ‘Obsessed with bypassing’ security.
The betting company suffered a huge loss of reputation, adding salt to the wound - this occurred just at the time of the 2022 Football World Cup, possibly creating a significant revenue loss for the company.
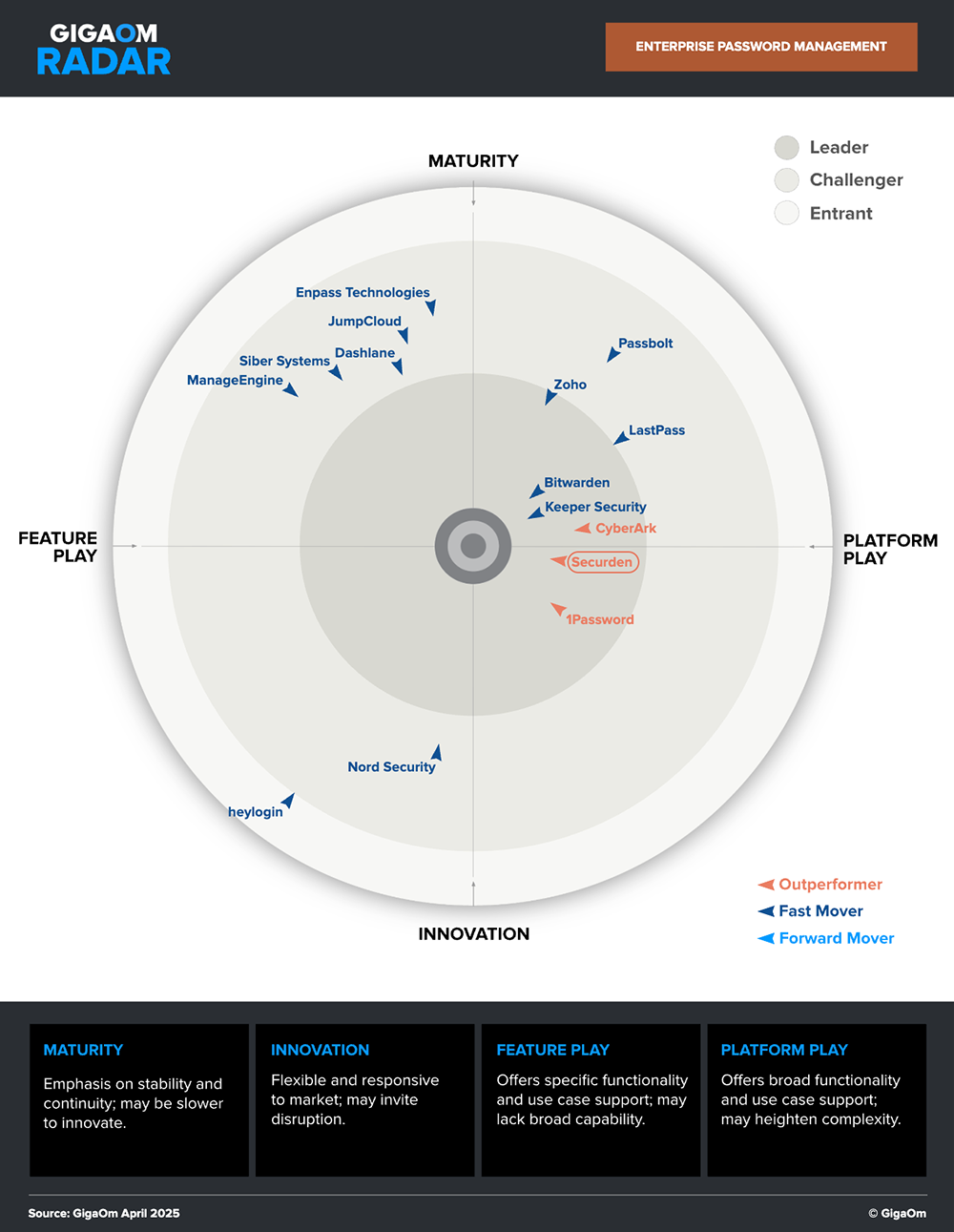
Securden is a market leader and an outperformer in the GigaOm Radar.
Organizations must understand the implications of weak Pa$$w0rds and take proactive measures
Organizations deal with a plethora of user and system passwords and must take precautionary steps to curb threats. Most of these risks can be mitigated by sticking to the basics of password hygiene.
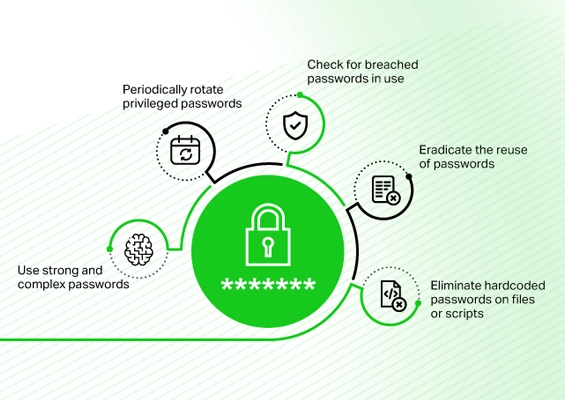
Enforcing password management best practices goes a long way in protecting businesses against new-age threats. Here are a few basic measures to take to ensure good password health:
Use strong and complex passwords - Login accounts, whether used personally or from a business perspective, should have strong passwords with more than 8 characters and comprise special characters, alphabets, and numerals.
Periodically rotate privileged passwords - Corporate accounts must change their passwords periodically, ideally once every 90 days.
Check for breached passwords in use - Passwords used within the organization must be checked regularly to ensure they are not part of previous breaches. Read more about Dark web monitoring.
Eradicate the reuse of passwords - As a rule of thumb, never utilize the same password across multiple logins or websites. All company passwords must be unique from each other.
Eliminate hardcoded passwords on files or scripts - Passwords must not be written down on paper, stored on Excel sheets, or hardcoded on scripts/applications. Passwords must instead be stored securely in a digital vault.
Even though this covers the basic aspects of password security, organizations often find themselves requiring advanced technologies and a wide variety of cybersecurity tools to protect their assets. Regardless of the advanced solutions that they deploy, not sticking to the basics costs them dearly.
Password security has established itself to be the building block of data security. Password management solutions help automate password management best practices, secure enterprise secrets and change compromised passwords that are in use.
Explore Securden’s Enterprise Password Vault
You can try Securden's Enterprise Password Vault for 30 days. Sign up for the cloud version or download the on-premise trial.



























![What is Cloud PAM? [Definition, Features, Benefits, and Factors to Choose the Right One]](/images/cloud-pam/cloud-pam-blog-image.webp)