Are all your privileged accounts really under control?
One unchecked admin account is all it takes to open the door to a significant security breach. That’s why IT security teams, CISOs, and compliance leaders rely on Privileged Access Management (PAM) to secure critical access points, monitor insider activity, and minimize human error.
To help you build a strong PAM foundation, we’ve created a comprehensive, field-tested PAM checklist based on industry best practices, competitive insights, and Securden’s expertise.
Whether you’re starting from scratch or auditing an existing setup, this checklist will walk you through every key stage of PAM implementation.
Use the PAM Implementation Checklist (Google Sheet)
Want to save or share the checklist with your team? Make a copy of this editable Google Sheet to assign tasks, track implementation, and prep for audits.
- Mark items as Complete (✓), Incomplete (✕), or N/A
- Add notes, assign owners, or link to documentation
- Review quarterly or after major infrastructure/security changes
Open the Checklist in Google Sheets
Looking to see it in action?
Why Do You Need a PAM Checklist?
Security breaches don’t send warnings. All it takes is one overlooked admin account to compromise your entire infrastructure. According to Verizon’s 2023 DBIR, 74% of breaches involved the human element, including the use of stolen credentials, privilege abuse, or social engineering attacks.
Let's face it—manual tracking of privileged accounts fails. Spreadsheets get outdated. People forget. Systems change. A structured checklist is the only failsafe tool that’ll help you catch what humans miss. Without a structured system, manual privileged access tracking breaks down, leaving backdoors open for attackers and auditors alike.
A PAM checklist helps you:
- Ask the right access-related questions (Who? Why? For how long?)
- Maintain consistency across IT and security teams
- Ensure no privileged access goes unreviewed
It’s not just a tool — it’s your insurance policy against privilege-related threats.
Understanding the fundamentals of privileged access management is essential before implementing these controls.
That’s why it’s imperative that modern businesses use PAM checklists to make sure they are on the right path to securing their digital assets.
5 Cybersecurity Risks PAM Checklists Can Help You Mitigate
Without a structured approach to managing privileged access, your organization faces significant security vulnerabilities. These aren't theoretical threats—they're the reality of today's digital landscape.
Silent privilege creep – Users accumulate unnecessary access rights over time, creating an expanded attack surface nobody's tracking.
Orphaned admin accounts – Former employees or contractors retain access long after their departure, creating backdoors into your systems.
Credential sharing – Multiple team members using the same privileged credentials, eliminating accountability and amplifying risk.
Lack of visibility – No way to detect unusual privileged activity or identify potential insider threats until damage occurs.
Compliance violations – Inability to demonstrate proper access controls to regulators, resulting in fines and sanctions.
These risks aren't just security concerns—they're business threats that can impact your bottom line, customer trust, and operational stability.
What are the Benefits of Using a PAM Checklist?
So, what makes a PAM checklist so valuable? It transforms vague security goals into concrete, actionable steps. A comprehensive PAM checklist provides:
Single source of truth – One definitive reference point for all privileged access policies and procedures.
Standardized implementation – Consistent security practices across departments, regardless of who's handling the implementation.
Streamlined audits – Ready documentation for compliance requirements, turning audit seasons from emergencies into routine processes.
Proactive risk identification – Regular reviews that catch access issues before they become security incidents.
Measurable security improvement – Clear benchmarks to track your progress in securing privileged accounts over time.
When security teams follow a well-defined checklist, they don't have to reinvent security protocols for every new system or wonder if they've covered all their bases.
The structured approach a PAM checklist provides doesn't just improve security—it makes security manageable. Instead of reacting to threats, you build prevention into your everyday operations.
A comprehensive PAM checklist transforms uncertainty into actionable security. Sleep better knowing you've covered your bases with a PAM checklist during the implementation. Let's figure out what should be on yours.
Still unsure how much of a difference a checklist can make?
Here’s how privileged access management compares with and without one:
PAM With vs. Without a Checklist
| Area | Without a Checklist | With a Checklist |
|---|---|---|
| Account Oversight | Admin and service accounts are scattered across teams with no central inventory. | All privileged accounts are documented, reviewed, and mapped to systems. |
| Access Requests | Requests are handled via emails or chats, often without approvals or documentation. | Standardized workflows ensure every access request is approved, justified, and time-bound. |
| Onboarding/Offboarding | Employees gain access ad hoc and rarely lose it when roles change or they exit. | Access is granted based on roles and automatically revoked during offboarding. |
| Audit & Compliance | Scrambling for logs and policies during audits increases the risk of penalties. | Auditable records, policies, and session logs are readily available for compliance checks. |
| Incident Response | No way to trace who did what — investigations take days or go unresolved. | Session monitoring and audit trails make post-incident reviews accurate and fast. |
| Credential Security | Shared passwords and manual updates leave critical accounts exposed. | Passwords are rotated automatically and stored securely in encrypted vaults. |
| Team Alignment | Security practices vary across teams — there’s no unified strategy. | Everyone works from the same playbook, reducing human error and policy gaps. |
A checklist doesn’t just guide the process—it transforms privileged access management into a controlled, trackable, and scalable security practice.
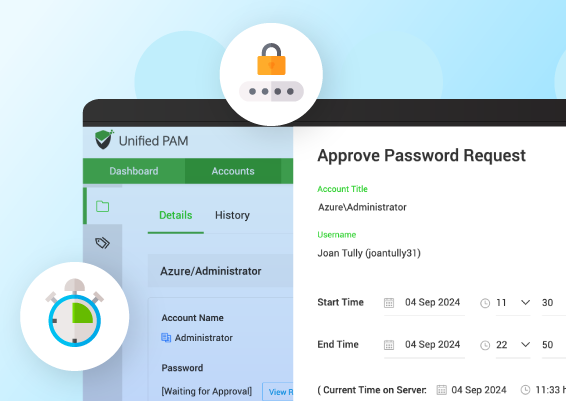
Secure Your First Step With Unified PAM
Start with a simple check and secure your most valuable assets. Make sure all privileged accounts are properly tracked.
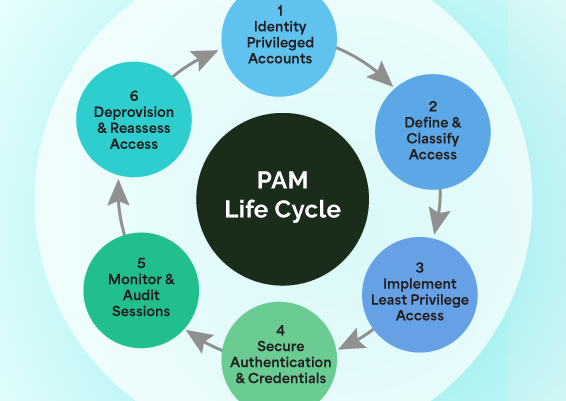
7-Stage PAM Checklist: Your Complete Implementation Roadmap
We’ve broken the process into 7 distinct, practical stages to help you plan, deploy, and evolve your PAM program with confidence.
Each stage of this checklist includes clear actions that your IT, security, and compliance teams can follow independently.
Stage 1: Pre-Implementation Planning
Before all else, you must create a solid foundation for your PAM system. This planning phase sets the direction for your entire PAM strategy.
Deployment Model: Consider whether a cloud-based, on-premises or hybrid solution best fits your needs.
What are your existing IT infrastructure and future plans? Cloud PAM offers flexibility but may raise data sovereignty concerns, while on-premises PAM solutions provide greater control but require more maintenance resources. Hence, you must consider it all before making your choice.
Scalability: Evaluate how the PAM solution will grow alongside your organization.
Record your current user and device count, then project growth over the next 3-5 years. The right PAM solution should accommodate this growth without requiring a complete overhaul.
Regulatory Compliance: Identify industry-specific regulations your PAM solution must address.
Document which compliance frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc.) apply to your organization and how your PAM implementation will help satisfy these requirements. Zero trust security principles are increasingly becoming compliance requirements in regulated industries. Many organizations also need to meet cyber insurance requirements that mandate specific privileged access controls.
Budget: Calculate both immediate and long-term costs.
Beyond the basic considerations, PAM pricing includes costs for training, integration with existing systems, and ongoing maintenance. Compare these against the potential cost of a breach to justify your investment.
Stakeholder Buy-In: Identify key decision-makers whose approval you'll need.
List the stakeholders from IT, security, legal, finance, and executive teams who need to approve the project, along with their specific concerns that must be addressed.
Stage 2: Inventory & Risk Assessment
Now that you've laid the groundwork, it's time to understand exactly what you're protecting.
Account Identification: Create a comprehensive inventory of all privileged accounts.
Document every account with elevated access, including administrative users, service accounts, emergency accounts, and application-specific privileges. This inventory serves as the foundation of your privileged account management strategy.
Access Mapping: Map each privileged account to the systems it controls.
For each account, list all systems, applications, and data it can access. Mapping the access each account wields helps visualize the potential impact if an account is compromised.
Risk Prioritization: Rank privileged accounts based on their potential impact if compromised.
Assign risk levels to each privileged account based on what sensitive data they can access. Access to your most sensitive data which includes access to critical infrastructure and financial systems typically warrants the highest risk ratings.
Third-Party Access: Document external parties with privileged access to your systems.
Catalog all vendors, contractors, and partners with privileged access, noting what they can access and why. Third-party risk often gets overlooked but remains a significant vulnerability point.
Stage 3: Policy Design
With your inventory complete, it's time to establish the ground rules of engagement for privileged access.
Access Rules: Define clear criteria for granting privileged access.
Document what constitutes "privileged access" in your organization and create role-based access profiles. Consider implementing just-in-time access to reduce the attack surface by providing privileges only when needed.
Authentication: Determine authentication requirements for privileged users.
Specify which privileged actions require multi-factor authentication, biometrics, or other enhanced verification. This creates additional security layers beyond passwords.
Shared Credentials: Establish protocols for managing shared accounts.
Document how shared accounts will be secured, potentially using a password manager for teams that provides vault capabilities and automatic rotation of credentials.
Emergency Protocols: Create clear procedures for break-glass scenarios.
Define what constitutes an emergency, who can authorize emergency access, and how this access will be monitored and revoked once the emergency ends.
Stage 4: Solution Deployment
Now comes the practical implementation of your PAM solution.
Integration: Ensure compatibility with existing identity systems.
Document how your PAM solution will integrate with active directory, existing IAM systems, and authentication mechanisms to create a seamless security ecosystem.
Testing: Validate functionality in a controlled environment.
Create a testing plan that verifies all critical PAM functions in a non-production environment before affecting real systems. Document test scenarios and success criteria.
High-Risk Targets: Prioritize critical systems for initial protection.
List your most sensitive systems and applications that should be brought under PAM control first, such as domain controllers, financial systems, and customer data repositories.
Automation: Identify processes that should be automated.
Specify which PAM processes will be automated, such as password rotation, access reviews, and account provisioning/de-provisioning. Automation reduces human error and ensures consistency in your privileged access governance framework.
Stage 5: Access Controls & Monitoring
With your solution deployed, you need advanced monitoring capabilities and controls to maintain security.
Least Privilege: Implement the principle of least privilege.
Document how you'll ensure users have only the access they absolutely need to perform their jobs. This cornerstone of zero-trust security significantly reduces your attack surface.
Session Monitoring: Enable comprehensive activity tracking.
Specify which privileged sessions will be recorded, how long recordings will be retained, and who can review them. This creates accountability and valuable forensic evidence.
Alerts: Set up notifications for suspicious activities.
Define which actions trigger alerts, their severity levels, and the response protocols for each. Early detection of unusual privileged activity can prevent or limit damage from attacks.
Audit Trails: Maintain detailed records of all privileged activities.
Document how you'll maintain comprehensive logs that tie specific actions to individual users and timestamps. These audit trails are crucial for compliance and investigations.
Stage 6: Training & Awareness
Technology alone isn't enough—people need to understand and follow your PAM practices.
Employee Training: Develop a comprehensive training program.
Outline how different user groups will be trained on PAM policies and tools. Consider using a mix of methods such as workshops, documentation, and simulations to accommodate different learning styles. Training should also cover the various PAM tools and their specific security functions.
Approver Training: Prepare designated staff for access request evaluation.
Document specific training for managers and others who approve access requests, ensuring they understand risk factors and can make informed decisions about granting privileges.
Incident Response: Establish clear reporting channels for security concerns.
Create step-by-step instructions for employees to report suspicious activities or potential policy violations. Prompt reporting can significantly reduce the impact of security incidents.
Stage 7: Maintenance & Evolution
PAM implementation isn't a one-time project—it requires ongoing attention.
Updates: Schedule regular maintenance of your PAM solution.
Create a calendar for system updates, security patches, and feature upgrades. Regular maintenance ensures your PAM system remains effective against evolving threats.
Policy Reviews: Plan periodic reassessment of access rules.
Set a schedule for reviewing and updating PAM policies to reflect organizational changes and emerging security practices. Quarterly reviews are common but adjust based on your organization's pace of change.
Disaster Recovery: Create contingency plans for PAM system failures.
Document backup procedures and recovery steps if your PAM system becomes unavailable. Ensure privileged users can still access critical systems during outages without compromising security.
Feedback Loop: Establish mechanisms to collect and implement user feedback.
This 7-stage checklist serves as a hands-on guide through your PAM implementation—from planning to daily operations and future audits. Whether you print it, bookmark it, or build it into your workflows, it gives your team a reliable system for managing privileged access securely and consistently.
Creating a reliable security framework that protects your most sensitive access points while maintaining operational efficiency is just a few ticks away. When working with a comprehensive PAM software like Securden’s Unified PAM, you can get your digital fortress up and running in no time.
Watch Over Your Assets With Unified PAM
Secure every access point with precise control. A focused approach to tracking privileges makes a real difference in your overall security.
Additional PAM Audit Checklist Elements to Consider
While our 7-stage PAM implementation roadmap covers the core framework, these additional elements serve as critical reinforcements for your privileged access security strategy. Here are a few questions you should try and answer to cover up the security gaps, if any, in your PAM strategy.
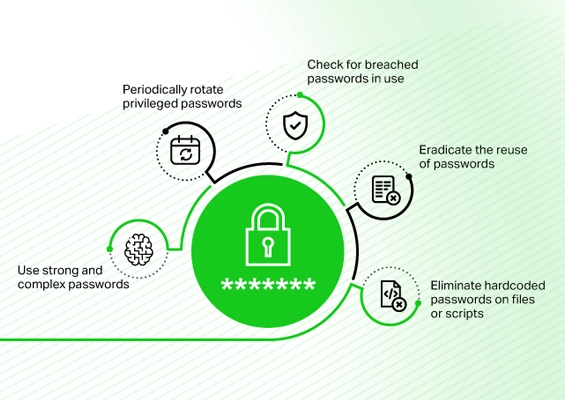
Strong Authentication & Password Management
Ask yourself
- Have you implemented multi-factor authentication for all privileged accounts?
- Do your password policies exceed basic industry standards?
- Are privileged credentials stored in encrypted vaults?
- Is automatic password rotation implemented for sensitive accounts?
- Can your system generate one-time passwords for temporary access?
Centralized Session Management
- Do you conduct regular reviews of access rights at least quarterly?
- Have you tested your PAM controls through simulated breach scenarios?
- Are you analyzing access logs to identify potential policy improvements?
- When was your last external audit of privileged access controls?
- Does your team regularly update PAM procedures based on new threats?
Policy & Compliance
- Have you mapped your PAM controls to your specific compliance requirements?
- Is there clear documentation for all privileged access policies?
- Do you have established approval workflows for privilege escalation?
- Are emergency access procedures documented with audit trail capabilities?
- Can you demonstrate consistent application of PAM policies during audits?
With these three final points, you can build a strong, compliant framework that’ll protect your organization on all fronts.
Incorporating these advanced checklist elements helps you move from reactive control to proactive security. From strong authentication to audit-friendly policies, every layer counts. Securden’s Unified PAM platform simplifies these complexities—offering built-in support for password rotation, JIT access, session logs, and audit-ready compliance workflows. Give our cybersecurity solutions a shot so that you can focus on the things that matter most to your business.
Bonus Download: PAM Audit Checklist (Quarterly Self-Check)
Your PAM implementation is complete, but is it still working as intended 3 months later?
Download our Quarterly PAM Audit Checklist — a structured, internal-use tool for security, IT, and compliance teams. It includes:
15 essential audit questions categorized across 5 key areas:
- Privileged account inventory & ownership
- Access controls & role review
- Session & credential management
- Compliance audit readiness
- Governance & KPI tracking
Each item includes a short explanation of why it matters, so your team can take meaningful action — not just check boxes.
Download the PAM Audit Checklist (Google sheet)
Tip: Use it every quarter to stay ahead of privilege-related risks and remain audit-ready year-round.
Build a Resilient Cybersecurity System With Securden
You’ve just walked through a complete PAM journey—from identifying privileged access needs to implementing controls and auditing them effectively.
Buyer’s Checklist → Know what to look for
Implementation Checklist → Step-by-step rollout
Audit Checklist → Ongoing validation and improvement
Every phase was designed to help your team move from reactive fixes to proactive security.
Securden’s Unified PAM platform brings this entire roadmap to life through a single, integrated solution. You get:
- Real-time session monitoring
- Just-in-time access
- Detailed audit logs
- Centralized credential vaults
- Offline access support
- Built-in compliance workflows
And unlike other platforms, Securden’s pricing is simple and user-based—no hidden fees, no upsell traps, and no paywalls blocking core security features.
Ready to see it for yourself? Sign up for a free 30-day trial today and experience how Securden’s Unified PAM can cross all your security concerns off the checklist, safeguard your critical assets, and keep your network secure 24x7.
Trusted by Security Teams Worldwide
A leading Swiss Bank Used Securden’s PAM solution We relied on manual processes for password management. Personal KeePass files were shared between teams, which was both time-consuming and prone to human error. We chose Securden for multiple reasons: its comprehensive feature set, ease of implementation, user-friendly interface, competitive pricing, straightforward upgrades, and easy management of high-availability nodes. - Paolo Bonfanti (Security Administrator)
Check Off Every Security Concern With Securden
Every step of our checklist works together to keep your access points secure and compliant. See how our user-based licensing means no hidden costs for extra features.
FAQs on the PAM Checklist
1. What are the common challenges when implementing a PAM checklist?
Most organizations struggle with accurately identifying all privileged accounts across complex IT environments, particularly legacy systems and shadow IT.
Another significant hurdle is securing executive buy-in for PAM initiatives, as stakeholders often underestimate privilege-based security risks until after an incident occurs.
2. How can I train my team to effectively use a PAM checklist?
Develop role-specific training modules that address the unique responsibilities each team member has in the PAM ecosystem, rather than generic security awareness.
Supplement formal training with hands-on workshops where staff can practice using PAM tools in realistic scenarios, and maintain up-to-date documentation that evolves alongside your security practices.
3. What are the best practices for maintaining compliance with a PAM checklist?
Create a dynamic compliance calendar that aligns your PAM checklist reviews with regulatory deadlines applicable to your industry and geography.
Conduct both scheduled and surprise audits to verify adherence to privileged access policies, and designate compliance champions within each department who can help translate regulatory requirements into practical security measures.
4. How can I automate the update process for a PAM checklist?
Implement PAM software with robust automation capabilities like Securden’s Unified PAM that can synchronize access policies across multiple systems when changes occur.
Configure automated compliance reports that flag discrepancies between your current PAM practices and your established checklist criteria, enabling proactive remediation before formal audits.
5. What metrics should I track to evaluate the success of a PAM checklist?
Track both leading indicators such as the percentage of privileged accounts reviewed quarterly and lagging indicators like the number and severity of privilege-related security incidents.
Measure the average time to revoke unnecessary access rights, compliance audit findings related to privileged access, and the reduction in orphaned admin accounts over time.
6. How often should I review and update my PAM checklist?
Conduct comprehensive reviews quarterly at a minimum, with focused reviews whenever significant changes occur in your IT infrastructure, business operations, or regulatory landscape.
After major security events in your industry, perform targeted reviews of checklist elements that relate to similar attack vectors to ensure your defenses remain relevant against current cyber threats.



























![What is Cloud PAM? [Definition, Features, Benefits, and Factors to Choose the Right One]](/images/cloud-pam/cloud-pam-blog-image.webp)