Never Trust, Verify Everything!
The “never trust" in the slogan may seem unsettling to many but you can’t deny that the Zero Trust slogan perfectly captures our reality.
The digital attack surface has grown exponentially as companies adopt cloud technology, expand their remote workforces, and enable employees to access critical data through mobile applications.
Traditional perimeter-based security models which worked fine in the pre-covid era, are no longer sufficient to safeguard your digital assets, sensitive data, and systems. Modern organizations need comprehensive cloud infrastructure security strategies to protect distributed environments. This vacuum has given rise to the Zero Trust Security model that can help you crack down across the hierarchy of your firm, verifying all access given to each employee, non-human identity, and third-party partner.
So, what does the Zero Trust strategy involve, and how can it shield your business from evolving threats? Read on to find answers to all the questions you may have about zero trust security.
What is a Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a security model that assumes no one or device should be trusted by default—whether inside or outside the network. Forrester Research Inc. first coined the term in 2010. The Zero Trust security framework aims to remove implicit trust by enforcing strict identity authentication and authorization throughout the network.
In simpler terms, you should treat all the requests to access resources as if they come from an untrusted network until they have been inspected, authenticated, and verified. By treating all connections as potential threats, you mitigate risks tied to insider threats and lateral movement within networks.
Do remember that Zero Trust is not a single technology but rather a philosophy that shapes how security frameworks are designed. It is a cloud security model that provides comprehensive, adaptable protection of distributed environments while still allowing secure access.
How Does a Zero Trust Security Model Work?
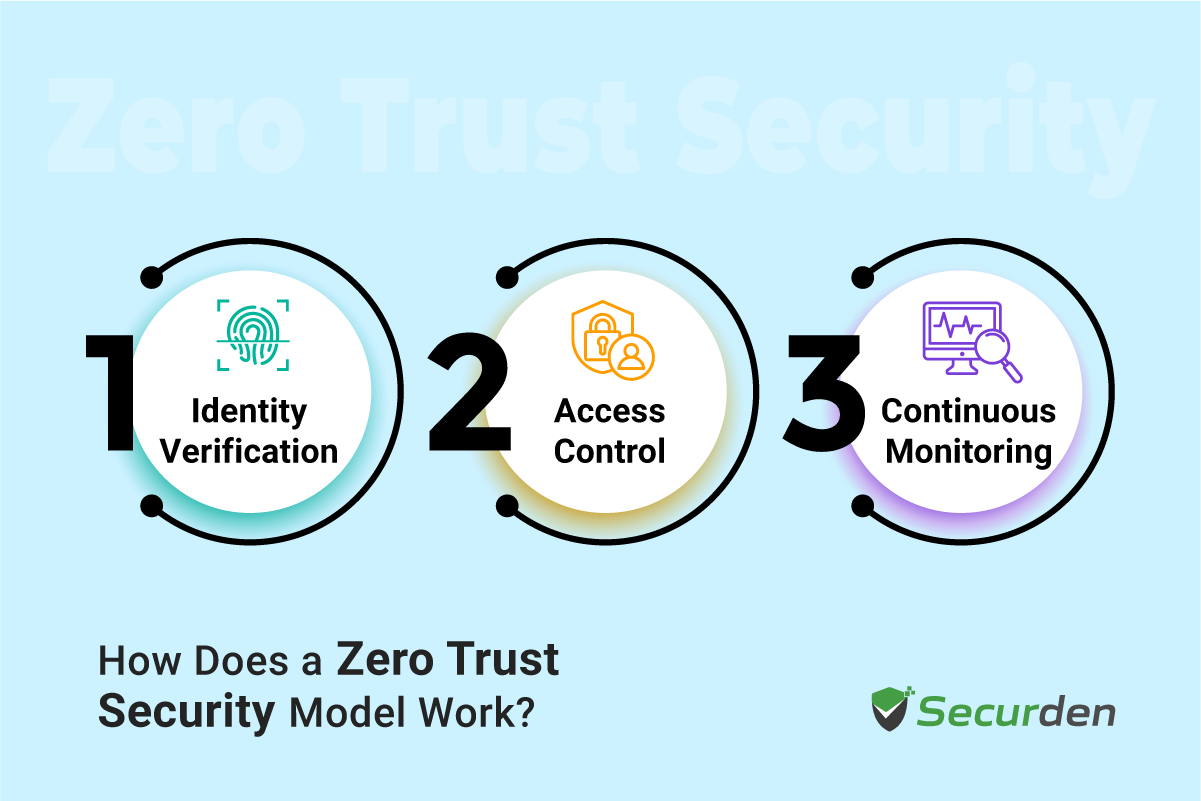
Zero Trust Security implements strict measures to ensure that nobody can access your sensitive resources and critical accounts without proper verification.
Here’s a breakdown of the Zero Trust security model’s core mechanisms:
- Identity Verification: Every access request requires authentication via multiple factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens. Identity verification ensures that only verified users can proceed.
- Access Control: Users and devices are granted the minimum level of access to perform their tasks, following the least privilege principle. This limits the scope of potential damage in case of a breach.
- Continuous Monitoring: Systems actively monitor all network activity for anomalies or unauthorized access attempts. Real-time alerts and automated responses can help contain potential threats swiftly.
All these mechanisms work together to provide a strong, adaptable security framework. By ensuring that every access request is verified, limiting user permissions, and continuously monitoring for threats, organizations can effectively protect sensitive data while maintaining secure user access.
Put Zero Trust to the Test With Securden
Ready to see how a Zero Trust approach can enhance your security? Set up a free PoC and experience Securden’s solutions firsthand.
What are the Core Principles of Zero Trust Security?
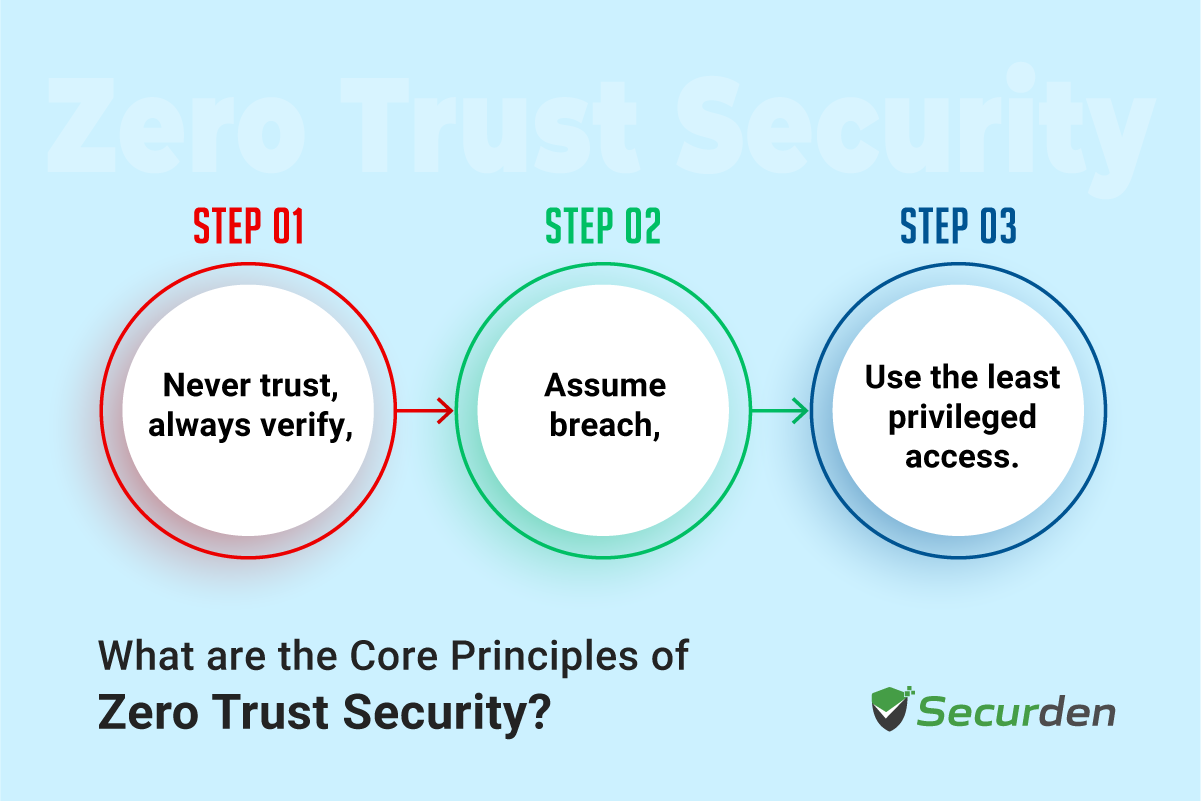
The Zero Trust model, at its core, is based upon three fundamental principles:
- Never trust, always verify
- Assume breach
- Use the least privileged access
These core principles of Zero Trust Security guide how security strategies are built and implemented, ensuring robust protection at every level of an organization’s infrastructure.
1. Never Trust, Always Verify
This principle emphasizes the idea that trust should never be assumed. Every access request, whether inside or outside the network, is treated as potentially malicious.
Verification involves using strong identity authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and assessing contextual factors like user behavior and device health. Organizations can reduce the chances of unauthorized access by consistently validating each request.
Example: A senior employee attempts to access sensitive financial data from a personal device while working remotely. The system requires multi-factor authentication (MFA) and checks the device's security posture before granting access, ensuring that only verified users can access critical information.
2. Assume Breach
Zero Trust operates on the premise that breaches are inevitable or may have already occurred. Instead of focusing solely on preventing external attacks, this principle ensures security measures are designed to contain potential damage.
This approach's key components are continuous monitoring, anomaly detection, and rapid incident response. Organizations stay vigilant and prepared by assuming a breach could happen at any time.
Example: A security team continuously monitors network traffic for unusual behavior, such as an employee accessing files they typically do not use. When an anomaly is detected, the team quickly investigates and isolates the account to prevent potential data exfiltration, assuming a breach may have already occurred.
3. Use Least Privilege Access
Granting users, devices, and applications only the necessary access minimizes the risk of misuse or accidental exposure of sensitive data. Organizations should implement zero standing privileges to ensure access is granted only when needed and automatically revoked when no longer required. This principle limits access rights based on roles, tasks, or specific timeframes.
Combined with technologies like role-based access control (RBAC), user account control and just-in-time (JIT) access, it ensures that access is tightly controlled and temporary when necessary.
Example: A project manager needs temporary access to a database for a specific task. Instead of granting full access indefinitely, the organization uses just-in-time (JIT) access to provide permissions that expire after 24 hours, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data exposure during that period.
The model relies on several foundational concepts in addition to the ones mentioned earlier, including:
That's where Securden comes in—delivering a unified approach to privileged access governance and security that helps you reduce risks and maintain control effortlessly.
.- Micro-Segmentation: Networks are divided into smaller, secure segments to isolate systems and data. This ensures that the threat cannot easily spread even if one segment is compromised.
- Secure Authentication: Strong, adaptive measures like MFA and single sign-on (SSO) verify users' identities and grant access only when conditions meet established security criteria.
These principles and concepts collectively enable organizations to avoid potential cybersecurity threats while maintaining secure and efficient workflows.
Now that we’ve explored Zero Trust's core principles, it’s time to consider the benefits of adopting this approach.
What are the Benefits of Zero Trust?
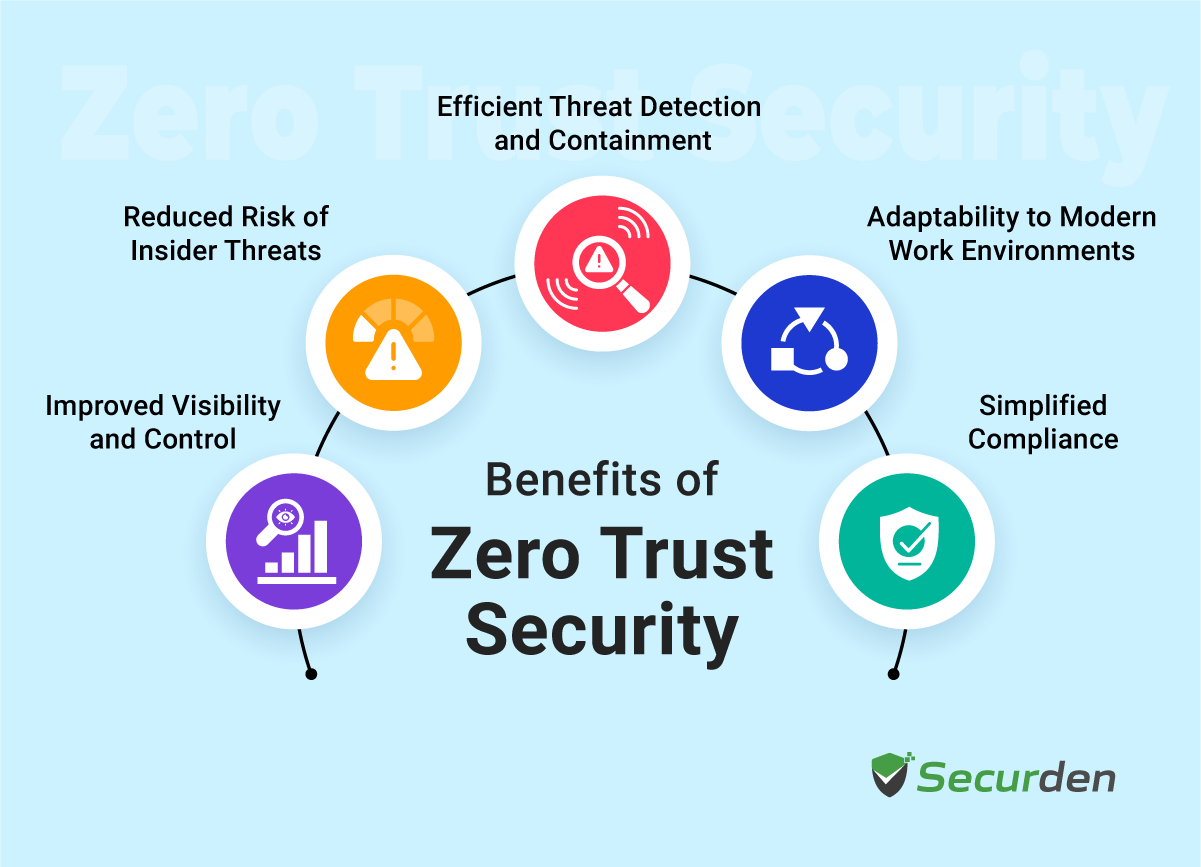
The Zero Trust security architecture helps organizations adopt a unified approach to protect their critical assets with comprehensive and adaptable strategies. Instead of relying on outdated network perimeter defenses, Zero Trust focuses on constant verification and stringent access management, tackling modern security challenges head-on while still allowing seamless access for users and devices.
Let’s look at the five key advantages the Zero Trust architecture brings to the table:
- Improved Visibility and Control: Organizations gain granular insights into network activities, allowing them to monitor who accesses resources, when, and from where. This visibility is crucial for detecting unusual activities and preventing security incidents.
- Reduced Risk of Insider Threats: By enforcing the least privileged access and zero trust policies, organizations can mitigate risks tied to insider threats, both accidental and malicious. Even if an attacker compromises user credentials, the blast radius of potential damage remains contained.
- Efficient Threat Detection and Containment: With continuous monitoring and segmentation, Zero Trust allows for rapid containment of data breaches or malware infections, limiting attackers' lateral movement within the network.
- Adaptability to Modern Work Environments: This model is well-suited for hybrid cloud environments and remote work setups, as it verifies every access request regardless of its origin, accommodating flexible work arrangements without compromising security.
- Simplified Compliance: Zero Trust provides complete visibility of network traffic and user behavior, which assists organizations in more effectively meeting compliance requirements like GDPR and HIPAA by maintaining detailed audit trails and real-time monitoring.
The Zero Trust principles help safeguard user identity, secure access points, and maintain a strong security posture across your organization's network.
With the key benefits established, let’s review the use cases of the Zero Trust strategy to better understand how you can implement it in your organization.
Bring These Benefits to Life With Unified PAM
Turn these benefits into reality for your organization with Securden. Let Securden show you how to make Zero Trust work for your organization.
Use Cases of Zero Trust Security Models With Real-Life Scenarios
Here are four distinct use cases to help you understand how you can mitigate cyber threats and safeguard sensitive data.
1. Secure Remote Access Without VPN
Zero Trust architecture and frameworks provide an alternative to traditional VPNs for remote access. Secure web gateways and secure access service edge (SASE) help ensure strong authentication and granular access controls without the vulnerabilities and performance issues associated with VPNs. The Zero Trust security strategy supports secure connections for remote workers while maintaining performance and security standards.
2. Application and Data Security
By implementing fine-grained authorization policies from the Zero Trust approach, organizations can ensure that only authorized users and devices have access to their critical resources, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is particularly important for safeguarding business-critical applications such as ERP systems, customer management platforms, or cloud storage solutions.
3. Third-Party Access Management
Organizations often need to grant access to third-party contractors or partners. Zero Trust Security allows for controlled access by verifying identities through identity and access management (IAM) tools and multi-factor authentication (MFA). This ensures that external users can only access specific resources necessary for their work, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive areas of the network.
4. Protection of IoT Devices
With 16.6 billion IoT devices in use by the end of 2023 and IoT analytics projections of 18.8 billion by 2024, securing these endpoints is crucial for all organizations. Zero Trust Security isolates IoT devices within network segments, limiting an attacker’s ability to move across the network if one is compromised. Continuous monitoring and strict access controls further safeguard against potential threats from these devices.
These use cases highlight how Zero Trust principles can adapt to modern security challenges, helping you maintain control, reduce vulnerabilities, and ensure your organization stays resilient against all cyber threats.
That brings us to the question, how can you implement it in your organization?
7-Step Guide to Implement Zero Trust Security
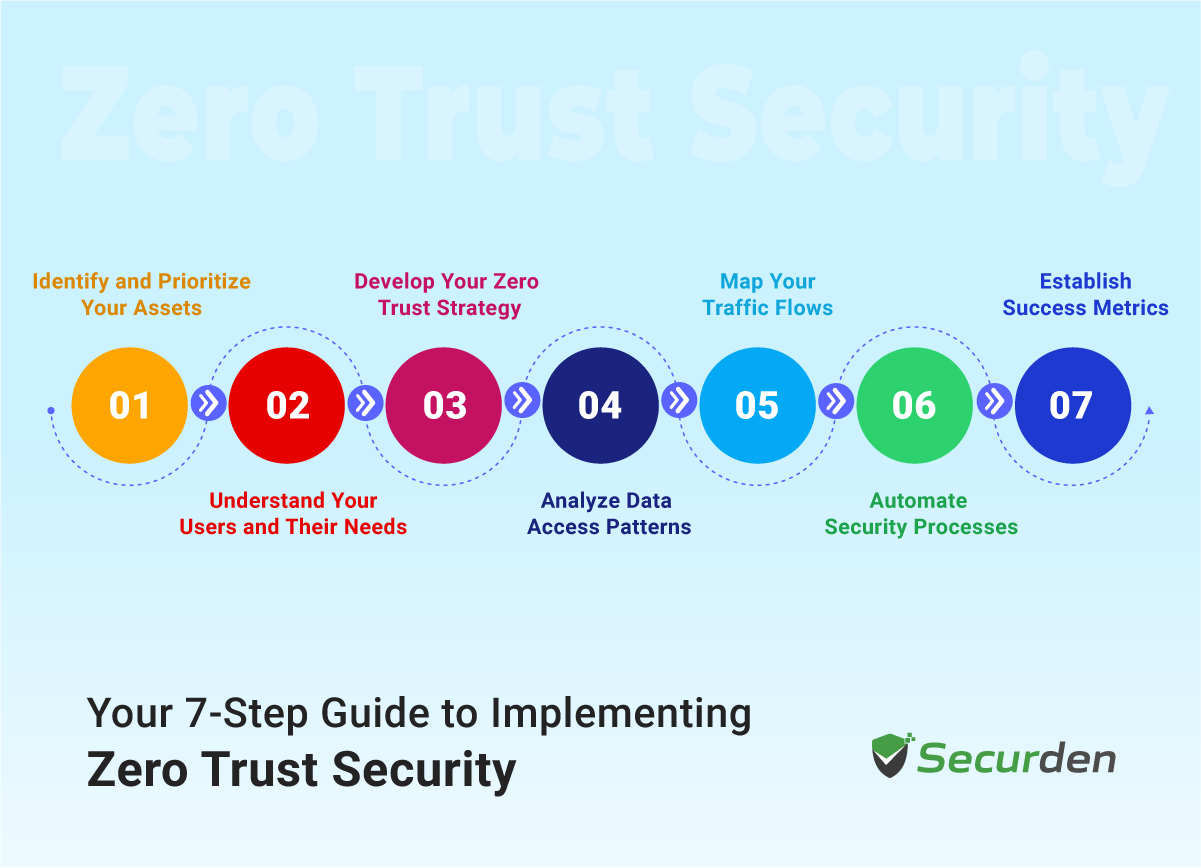
Zero Trust Security isn’t a plug-and-play solution or something you can install and forget. It is a multifaceted approach that involves identity and access policies, security solutions, workflows, automation, and network infrastructure. Although it may sound very complicated, you don’t have to worry; we have simplified it for you.
Here’s a 7-step guide for implementing Zero Trust security in your organization.
1. Identify and Prioritize Your Assets
Before you can protect anything, you need to know what you have. Start by taking stock of your digital assets—this includes sensitive data, applications, and systems that are critical to your operations. Create a detailed inventory that highlights which assets are most valuable and vulnerable.
2. Understand Your Users and Their Needs
Next, you need to figure out your users and their requirements. Who needs access to what? Map out all employees, contractors, and partners who interact with your assets. Gather information about their roles and access requirements. This step is crucial for managing user identities and ensuring access privileges align with their needs.
3. Develop Your Zero Trust Strategy
With a clear understanding of your assets and users, it’s time to work out your Zero Trust strategy. Think about how you will set up your security measures to reduce risks effectively. Take into account your budget, available IT resources, and the complexity of your existing infrastructure as you set a timeline for implementation phases.
4. Analyze Data Access Patterns
Data is at the heart of Zero Trust. Conduct a thorough analysis of how data is accessed across your systems. Look for anomalies—unusual access patterns or attempts to reach sensitive information outside established policies can indicate potential threats. Recognizing these patterns early can help you bolster defenses against data theft.
5. Map Your Traffic Flows
Understanding how data moves within your network is essential. Identify dependencies between users, applications, and databases containing sensitive information. Ask yourself: does every user or system that accesses this database truly need that level of access? Performing this exercise will help refine your access controls.
6. Automate Security Processes
Automation is key in the Zero Trust model. Implement tools that can monitor resources and activities continuously without overwhelming your IT staff. Solutions like Unified PAM that come loaded with advanced features like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are key to providing secure access while reducing manual oversight.
7. Establish Success Metrics
Finally, define how you will measure the success of your Zero Trust implementation. Set key performance indicators (KPIs) such as reductions in access privileges, increases in MFA usage, and overall stakeholder buy-in. These metrics will help you track progress and make adjustments as needed.
While these steps do set the stage, they are but a road map for the implementation, they don’t guarantee success. It’s time to take a look at the best practices to improve your chances of success and to streamline and improve your Zero Trust strategy.
Turn Zero Trust Security Plans Into Action
Let Securden help you execute your Zero Trust roadmap. Use our tools to turn your Zero Trust strategy into a secure reality.
7 Best Practices for Adopting the Zero Trust Architecture
Whether you’re starting from scratch or refining your existing framework, here are five best practices that’ll help you stay on track:
1. Follow Established Standards Like NIST 800-207
Why reinvent the wheel, when you can access successful standards like NIST SP 800-207, CISA guidelines, DISA standards, or NCSC recommendations? If you are ever in doubt, let the well-established models guide you. Following these standards, you can foolproof your strategy and see to it that it’s built on proven principles, covering everything from secure access policies to data protection measures.
2. Adopt a Phased Approach
Zero Trust isn’t something you can implement overnight. Instead of trying to overhaul everything at once, focus on one area at a time. Start with the most critical assets or high-risk zones and gradually expand. Following a step-by-step method minimizes disruptions while keeping progress steady.
3. Make It Frictionless for Users
Security shouldn’t come at the cost of user experience. Implement seamless solutions like Single Sign-On (SSO) and adaptive multi-factor authentication (MFA) to maintain strong security while ensuring users can work efficiently. The goal is to secure access without creating unnecessary hurdles.
4. Deploy Automation for Policy Management
Manually updating access policies can make it prone to errors. Automating tasks like privilege adjustments based on user behavior or updating policies in real time ensures your security remains dynamic. Tools like Unified PAM and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can help streamline this process.
5. Continuously Monitor and Validate
Zero Trust is all about “never trust, always verify.” Continuously monitoring user and device activity ensures that access remains aligned with current roles and conditions. Regularly validate attributes like device health, location, and behavior patterns to stay ahead of potential threats.
6. Secure Workflows and Data Across Hybrid Environments
Modern businesses, more often than not are operating across on-premises systems, public clouds, and hybrid environments. Your Zero Trust architecture should extend to all workflows and data, ensuring consistency in security policies regardless of where operations occur.
7. Regularly Evaluate and Evolve
Threat landscapes change, and so should your Zero Trust framework. Conduct periodic assessments to identify gaps or outdated policies, then adapt your approach accordingly. A static Zero Trust model is a vulnerable one.
The right set of tools and technology, equipped with the core foundational principles, the step-by-step guide, and the best practices, is all you need to get started on the implementation.
And you’re in luck because Securden is just the partner you need for a successful Zero Trust architecture implementation in your organization. With its comprehensive solutions like Unified PAM and Enterprise Password Manager, Securden can help you improve your security posture and create a frictionless working environment while you are at it.
Build a Zero Trust Environment With Securden
Building a Zero-Trust environment starts with a clear strategy and the right technology partner.
That’s where Securden comes in—delivering a unified approach to privileged access governance and security that helps you reduce risks and maintain control effortlessly.
With Unified PAM and Enterprise Password Manager solutions, Securden centralizes privileged access, secures credentials, and simplifies compliance. Our advanced PAM features include just-in-time access, password vaulting, endpoint privilege management, secure remote sessions, and multi-factor authentication. These tools, backed by the support of our PAM experts, make implementing Zero Trust security achievable for businesses of all sizes.
Get ready to fortify your defenses and build a Zero-Trust environment. Contact Securden today to discuss how we can help you achieve a Zero-Trust architecture that protects what matters most.
Start Building Your Zero Trust Environment Today
Want to see how Securden can secure your digital assets? Set up a free PoC and experience the transformation firsthand!


